Iowa R&D Credit
Optimize your federal and Iowa R&D credit with TaxRobot.
Maximize your State Credits today!
Put the R&D tax credit process on autopilot.
Trusted By:








Iowa R&D Credit
Discover your eligibility for Iowa R&D tax credits and supercharge your enterprise.
Are There R&D Tax Credits in Iowa?
Iowa is a great place when it comes to tax credits and incentives for businesses. So, yes, there are tax credits available for R&D in Iowa. Companies engaging in research and development can take advantage of the Research Activities Credit.
This tax credit exists alongside other programs designed to reward businesses. For example, the High-Quality Jobs program is one of these. This allows companies to take advantage of a Supplemental Research Activities Credit.
Federal R&D Tax Credit
There are many programs out there to help businesses. Everything from government loans to tax credits can be found if a company knows where to look.
The federal R&D tax credit is designed to reward companies for investing in research and development. The goal is to encourage them to grow by spending money on activities that help them. This will help the economy grow in turn and, hopefully, will have an effect that leads to the creation of more jobs.
All of this is done by measuring qualified research expenses. These are expenses the government designates as helping with this goal.
The federal R&D tax credit is calculated by taking 20% of the qualified research expenses that exceed the base amount. This 20% is the amount of the credit. So, more qualified research expenses lead to a greater tax credit.
Research Activities Credit
The Iowa Research Activities Credit is designed with this federal credit in mind. It also allows for a tax credit based on qualified research spending above a certain amount. However, the exact numbers that go into this calculation differ, and some additional restrictions apply.
The Iowa credit is fully refundable and is defined as 6.5% of qualifying research expenses exceeding a base amount or 50% of qualifying research expenses, whichever amount ends up being lower. In most cases, this puts the credit around or at least close to 6.5%. In addition, another method of calculation. This method, the Alternative Simplified method, is simply 4.55% of qualified expenses made over the last three years.
The big restriction placed on the Iowa credit is that only qualified research expenses made within Iowa count toward this credit. So, if a company spends money on research in other states, this cannot be counted toward the Iowa credit.
Some companies can also take advantage of a Supplemental Research Activities Credit. This rewards companies with another credit worth 10% of their qualifying research expenses in cases where gross revenue is less than $20 million, or 3%, in cases where gross revenue is over $20 million.
Eligible Businesses and Industries
The Iowa R&D credit places a few limits on the types of industries that can claim the credit. The businesses must be involved in manufacturing, life sciences, software engineering, or aviation & aerospace.
Alongside this requirement, they also need to have eligible expenses. These are qualifying expenses made toward research and development.
Eligible Expenses
The Iowa definition of eligible research expenses is the same as the federal definition. The only stipulation is that the expenditures have to take place within Iowa. So, any expenses laid out in the federal program that happen within Iowa apply here and would make a business in a relevant industry eligible for the credit.
Maximize Your Iowa R&D Credit with TaxRobot
The Iowa R&D tax credit comes with plenty of unique stipulations and fine details. It also exists alongside other programs that influence and even change some of the calculations involved in the tax credit application process.
Luckily, TaxRobot can help. We have a complex and powerful tax credit software program. This allows us to create accurate tax credit applications designed to help businesses get the most out of the system. With us, you can become a master of the Iowa R&D tax credit.
Find Out How Much You Could Save
Curious about how much TaxRobot could help you save with the R&D credit? Use our calculator to find out.
Take a sneak peak
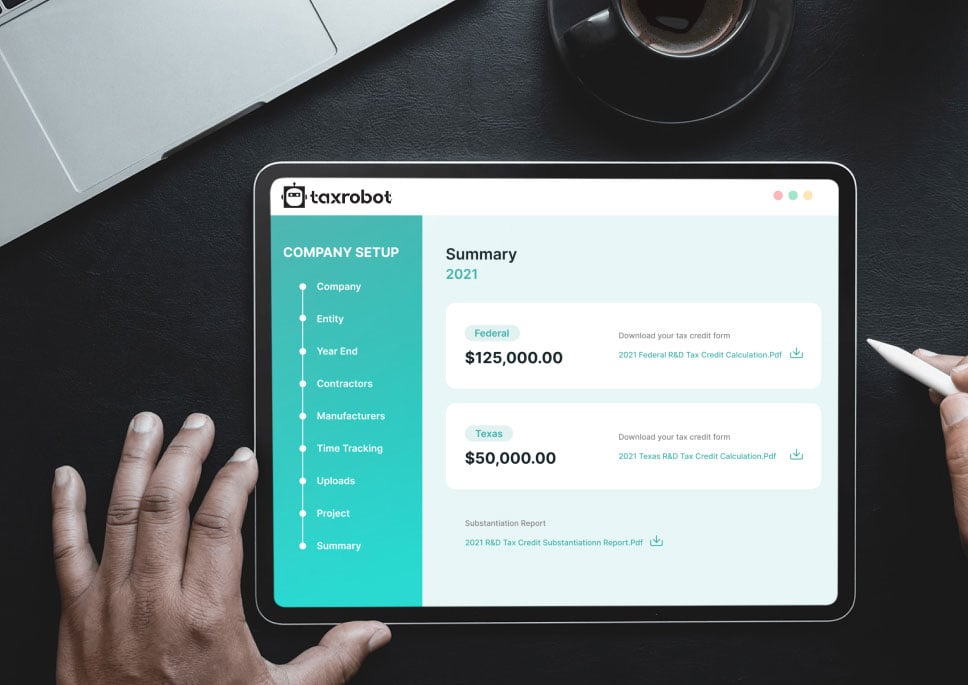
- Limited Time Offer
- Simple Onboarding
- Easy to Use
R&D Tax Credits FAQs
The four-part test as outlined in the Internal Revenue Code is used to determine qualified R&D activity.
The Four-Part Test
1). New Or Improved Business Component
Creation of a new product, process, formula, invention, software, or technique; or improving the performance, functionality, quality, or reliability of existing business component.
- Construction of new buildings or renovation of existing buildings
- Invention of a software application
- Manufacturing of a new product or the improvement of the production process for an existing product
- Creation of design documentation
2). Technological In Nature
The activity fundamentally relies on principles of the physical or biological sciences, engineering, or computer science. A taxpayer does not need to obtain information that exceeds, expands or refines the common knowledge of skilled professionals in a particular field.
- Physics (relationship between mass, density and volume; loading as the
result of gravitational attraction) - Engineering (mechanical, electrical, civil, chemical)
- Computer science (theory of computation and design of computational systems)
3). Elimination Of Uncertainty
Uncertainty exists if the information available to the taxpayer does not establish the capability or method for developing or improving the business component, or the appropriate design of the business component.
- The capability of a manufacturer to create a part within the specified tolerances
- The appropriate method of overcoming unsuitable soil conditions during construction
- The appropriate software design to meet quality and volatility requirements
4). Process Of Experimentation
A process designed to evaluate one or more alternatives to achieve a result where the capability or method of achieving that result, or the appropriate design of that result, is uncertain as of the beginning of the taxpayer’s research activities.
- Systematic process of trial and error
- Evaluating alternative means and methods
- Computer modeling or simulation Prototyping Testing
The R&D tax credit is one of the most misunderstood tax incentives available. Considering the myriad of industries and activities that legally qualify for the credit, the term “research and development” is a misnomer. Additionally, the R&D tax credit requires specialized knowledge and technology to identify and calculate the incentive properly.
Companies of various industries are unaware that they are eligible to claim the R&D tax credit. Under the Internal Revenue Code’s definition of R&D, many common activities qualify. You can get tax benefits for industries including software, technology, architecture, engineering, construction, manufacturing, and more.
The R&D tax credit can be claimed for all open tax years. Generally, open tax years include the prior three tax years due to the statute of limitations period. In certain circumstances, the law allows businesses to claim the R&D tax credit for an extended period of time. It is common for companies to amend previous tax years to claim this benefit and reduce the maximum amount of tax liability.
Partnerships and S corporations must file this form to claim the credit. The credit will flow from the Form 6765, to the Schedule K-1, to the Form 3800 on the individual’s tax return. For individuals receiving this credit that have ownership interest in a partnership or S corporation, Form 6765 is not required on the individual return.
Individuals claiming this credit can report the credit directly on Form 3800, General Business Credit if their only source for the credit is a partnership, S corporation, estate, or trust. Otherwise, Form 6765 must be filed with the individual’s tax return (e.g. sole proprietorship).
For tax years prior to 2016, the credit can be used to reduce the taxpayer’s regular tax liability down to the tentative minimum tax. The credit cannot be used to offset alternative minimum tax. Beginning in tax year 2016, eligible small businesses have expanded utilization for the credit. For these eligible small businesses, the regular tax liability can offset alternative minimum tax using the “25/25” rule.
What our customers have to say
I highly recommend TaxRobot to anyone considering an R&D Tax Credit software to complete their analysis.

We decided to switch to TaxRobot… Best decision we’ve ever made. More affordable, and less complicated.

I couldn’t believe how easy it was! In under an hour, we saved enough money to hire a new employee.
